Paper Dissection : When does loss-based prioritization fail?
In this post I discuss about a paper which studies about the scenarios where loss based prioritization method fails to account when there are noisy / corrupted examples in the training data by inducing noise in the training data.
Introduction and Motivation
Recently there has been a rise in the size and cost in training deep neural networks and this has led to hinderance in democratizing the machine learning research. Researching on efficient methods for training is of utmost importance. There has been several research direction on reducing the training time by seperating distribution clusters in the training set by their contribution in training. These mainly revolves around the fact that higher loss valued examples contribute more to training.
There are two types of examples that contribute to high loss in any training set :
- Low frequency or difficult examples.
- Corrupted or noisy or mislabeled examples.
And the loss based prioritization if done on a training regime, will not work on the latter type of examples and might even result in degradation of the final model.
This paper discusses the robustness of loss based sampling methods to varying level of dataset noise and corruption.
These are the ways to create an artificially corrputed examples :
- label Randomization
- Pixel shuffling
- Replacing inputs with Gaussian noise.
And all these corrpution when done, its difficult for a human to identify the target class and cosequently introduces stochasticity that mapping cant be learnt by human.
This paper mainly discusses on two types of loss based sampling methods :
- Selective Backrprop. (SB)
- Variance reduction importance sampling.
Both of these methods derails under supervised learning tasks with corrputed noise with Selective backprop degrading more rapid than variance reduction methods.
Loss-based Sampling Methods
let x_i and y_i be the i’th example in a supervised setting where x_i represents input tensor and y_i label. let f_w represent a nn model parameterized by learnable parameter w and L being the cross entropy loss. The goal is to find :
\[{w}^{*} = \underset{w}{\operatorname{argmin}} \frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} L(f_w(x_i),y_i)\]and the training regime for a stochastic gradient descent for a mini batch with a uniform sampling without replacement having \({\eta}_t\) as the learning rate with all the examples being treated equally :
\[{w}_{t+1} = {w}_t - {\eta}_t\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} {\nabla}_w L(f_w(x_i),y_i)\]Selective backprop (SB)
SB is a framework which prioritize learning high loss examples every iteration. In the original paper, SB converges 3.5X faster than the standard SGD and can further accelerated by using stale forward pass information.
SB maintains a moving histogram of size H and a buffer of candidate examples. At each iteration, SB computes loss for each examples and then fed to a function which provides the probabilty that it should be sampled. Samples are pushed into a buffer. When buffer size becomes greater than B, the first B examples are used for gradient updates.
The probablity of each example is calculated by CDF/Cumulative distribution function of its loss from the histogram : (so more the loss , more the probability of that example getting selected.)
\[P(L(f_w(x_i),y_i)) = CDF(L(f_w(x_i),y_i))^{\beta}\]Here, \({\beta} >= 0\) is a hyperparameter, controls the selectivity of the examples.
- \({\beta} = 0\) corresponds to all samples being selected for backprop.
- \({\beta} = 1\) corresponds to \(50\)% of samples being selected and so on.
Variance Reduction Importance Sampling
One of the reference paper (Katharopoulos & Fleuret, 2018) proposes a method where it tried to sample a bunch of examples that reduces the variances of gradient estimates. Similar to the SB method, This method maintains a set of presampling examples. Once the size reaches a threshold B (a hyperparameter) the algorithm samples a distribution proportional to the their loss values.
In paper : For experimenting purpose , test is done only on loss based, no uplifting weights/nowarmup for importance sampling is done.
Experiments
CIFAR 10 is used for evaluating the loss based prioritxation method : Selective backprop and Variance reduction importance sampling. But how to create a noisy example set?
Creating noisy examples :
Given \(D_{train}\) and \(D_{test}\) as train and test datasets respectively, and \(f_w\) as the nn model trained on \(D_{train}\) with \(w\) being the learnable parameters, the objective is to modify \(D_{train}\)
These are the following modifications to \((x_i, y_i)\) which were done to analyze the robustness of loss based on prioritization :
- Random Labels: In this case for an example \((x_i, y_i)\), the \(y_i\) is replaced by \({y}_i^`\) where \({y}_i^` \in (1...K)\) Where \(K\) is the number of classes.
- Shuffled Pixels : A single random permutation \(p\) is chosen and applied to each \(x_i\) to make it \(x_i^`\).
- Gaussian noise : \(x_i\) is replaced with \(x_i^`\) where each pixel is replaced by sampling a gaussian distribution with mean and variance similar to that of \(x_i\)
Results :
Evaluation was done on CIFAR10 with both of the methdods of training. The model that was considered for training was a wider residual network, with hyperparameters being : depth=28, widen factor = 10, batch size = 128, lr = 0.1 and momentum = 0.9 with SGD optimizer and weightdecay = 0.0005 num epochs was 100 with a drop in lr @ 60 and 80 epochs. The results are tabulated in Table 1 for no modification, 25% modification and 50% modification for all the methods : pristine, SB and variance reduction.
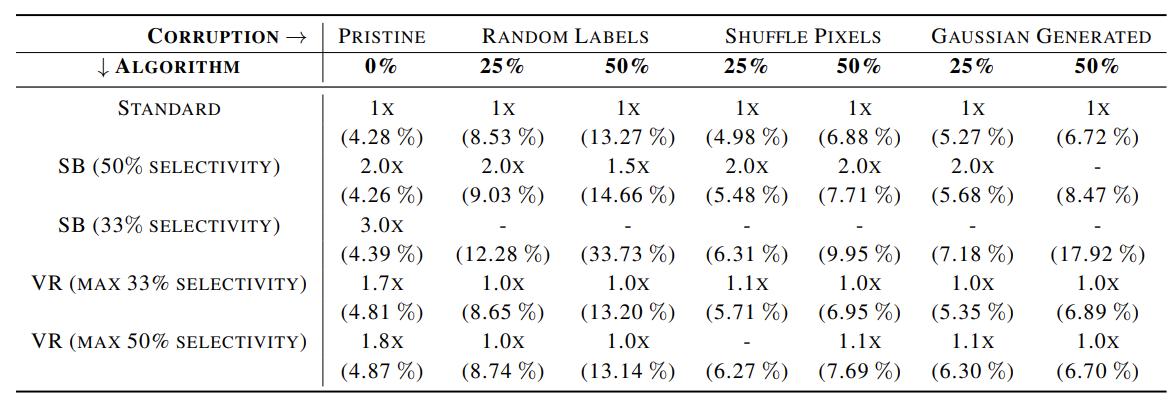
Table 1. Speedup and error rate of various methods under different datasets
Dash(-) in the table indicate that the method could not reach the threshold error for that method. With no corruption, both SB and VR improve training speed to reach the threshold error. But with the degradation, some time it falters / attains worse test error. Noticebaly, among both the methods, VR seems to be less affected with the corruption than SB.
For more detailed info about the project, please refer to the arxiv link here : here.